Asynchronous Programming in .NET: Understanding async/await
Understanding async/await:
In the world of .NET development, asynchronous programming has become a crucial aspect for building responsive and scalable applications. The async and await keywords introduced in C# make it easier to write code that performs asynchronous operations without the complexity of managing threads manually.
An Overview of Async/Await
Async Method Declaration
When you declare a method with the async keyword, you signify that this method will contain asynchronous operations. The return type of an async method is typically Task or Task<T>.
Await Expression
The await keyword is used to indicate that the following expression is an asynchronous operation. It allows the method to pause and wait for the asynchronous operation to complete without blocking the thread.
Control Flow in Async/Await
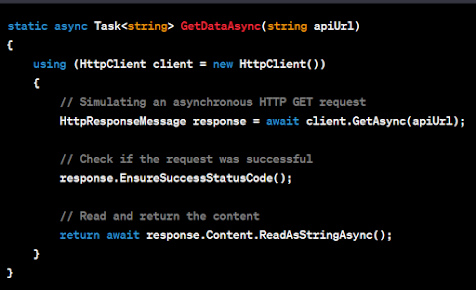
Let's consider an example of fetching data from an API using HttpClient to understand how control flows with async/await.
Main Method Call:
- The
Mainmethod is called, and it starts executing synchronously until it encounters the asynchronous methodGetDataAsync.
- The
GetDataAsync Method:
- When
GetDataAsyncis called, it begins executing synchronously until it reaches theawaitkeyword. - At the
awaitkeyword,GetDataAsyncreturns control to theMainmethod, allowing it to continue with other tasks.
- When
Main Method Continuation:
- While waiting for the asynchronous operation to complete, the
Mainmethod can perform other tasks or yield control back to its caller (if any).
- While waiting for the asynchronous operation to complete, the
Async Operation Completion:
- When the asynchronous operation (
client.GetAsync(apiUrl)) completes, the control returns to the point immediately after theawaitkeyword in theGetDataAsyncmethod.
- When the asynchronous operation (
Result Handling:
- The result of the asynchronous operation is then processed. In this case, it's the content of the HTTP response, which is read asynchronously using
response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync().
- The result of the asynchronous operation is then processed. In this case, it's the content of the HTTP response, which is read asynchronously using
Final Result:
- The result is returned to the
Mainmethod, and the execution continues from the point where it was paused.
- The result is returned to the
Behind the Scenes: Multiple Threads
While the example might not explicitly show the use of multiple threads, the asynchronous programming model in .NET abstracts away the complexity. Asynchronous operations often involve I/O-bound work, and the .NET runtime efficiently manages threads, potentially using a thread pool.
By leveraging the async and await keywords, developers can write code that looks synchronous, making it more readable and maintainable, while the runtime handles the intricacies of managing threads and asynchronous tasks.
In conclusion, understanding the control flow and the use of multiple threads in asynchronous programming is essential for building high-performance and responsive .NET applications. The async and await keywords empower developers to write code that is both efficient and readable.
for more click here
Happy coding!


Comments
Post a Comment